TAKING ON TESTS: Atlanta School Students Still Recovering From Cheating Scandal
Atlanta’s infamous public school cheating scandal sent some educators to jail last year and forced the system to clean up its culture of pressure-driven testing. But after the educators were found guilty of changing tests answers and sentenced, thousands of innocent victims remained: school children.
Some students had academic deficiencies that were never discovered or addressed. And as the most recent graduates prepare now for college or careers, some Atlanta Public Schools continue programs to re-mediate and support though challenges still remain.
Lawyers pleaded for leniency, and a judge flailed his hands in disgust in the April 2015 sentencing of Atlanta educators, guilty of cheating to boost student test scores. That’s the way they got bonuses or, in many cases, held on to their jobs.
Educators had funding, job evaluations, and more tied to student performance on the Criterion Referenced Competency Test or CRCT. For Sandra Harper Gallashaw’s daughter, Shandreamer, the impact of the cheating scandal is real. Her daughter attended Parks Middle School — the one where the principal testified he orchestrated cheating to protect his job. After the scandal erupted, she says the school was unstable.
“They have removed so many teachers,” says Gallashaw. “It was said that when they removed 178 people that were involved in the scandal that we would have professional people to teach our children, but all they gave us was substitute teachers — people coming and going,” she continues.
When her daughter went to high school, Gallashaw says the stigma followed her.
“It’s been a struggle because when she first got to Carver — how the teacher treated her. They knew these children were from the cheating scandal,” says Gallashaw. “And she actually quoted one of her teachers saying they should have taught her that at Parks.”
Gallashaw says her daughter had a tough time in some high school classes. She wanted to go to Tuskegee University in Atlanta, but didn’t get accepted. Now she’s considering going to the Navy.
A recent study from Georgia State University backs up Gallashaw’s assumption. Dr. Tim Sass says his research shows students were permanently damaged by efforts made to make them look better on paper.
“It appears that having their scores manipulated in the past led to lower student achievement, particularly in language and reading,” says Sass. “The reduction achievement we found was on the order of somewhere between a quarter and a half year of typical student learning.”
His study found as many as 7,000 students were potentially harmed by the scandal, and about half of them are still in school. Dr. Alicia Hill, an administrator for one of the Atlanta Public Schools programs designed to help cheating scandal students, uses Sass’s data to help students through a program called Target 2021.
“The program is geared toward the students who are potentially affected by the CRCT erasure in 2009,” Hill says. “That’s our response to make sure we are providing students with our support throughout graduation or the time that they graduate to make sure that they’re college and career ready.”
Atlanta has tried a variety of academic recovery and remediation efforts in recent years. Sandra Gallashaw has had two daughters graduate from the school system, and said she has doubts about its efforts.
“They haven’t tried enough,” Gallashaw says. “Just Saturday School for the high school students. One day out of how many years these folks been cheating. Just one day? It’s a smack in the face.”
Hill acknowledges there are challenges and criticism.
“We have lots of challenges and skepticism and there will be criticism, but also success is knowing that as we are getting this off the ground and running. There are people who are saying ‘This is great. I’m glad you are doing something,’” Hill says.
The school system is spending $9 million to support students through programs like Communities in Schools, or CIS, headed by Frank Brown.
“We are actually case managing every one of these students and making sure that if they have needs that are academic in nature,” Brown says. “We are sending them to tutoring.”
Yet, he says, it takes more than just tutoring to serve and support the students who attended schools that were part of the cheating scandal.
“We bring an array of CIS services. That’s drop out prevention programming, anti-bullying campaign. AT&T wants to do career exploration. Anytime something like this happens and it has nationwide attention, there’s a sensitivity there,” he says. “Parents want to know what I can get my child to get them where they need to be academically and emotionally. How can we get control of this horrific situation that they had no control over.”
The last group of students potentially impacted by the cheating scandal is projected to graduate in 2021. And while the verdict for the educators has been decided, seven years after the scandal broke — the actual verdict for the students still is uncertain.
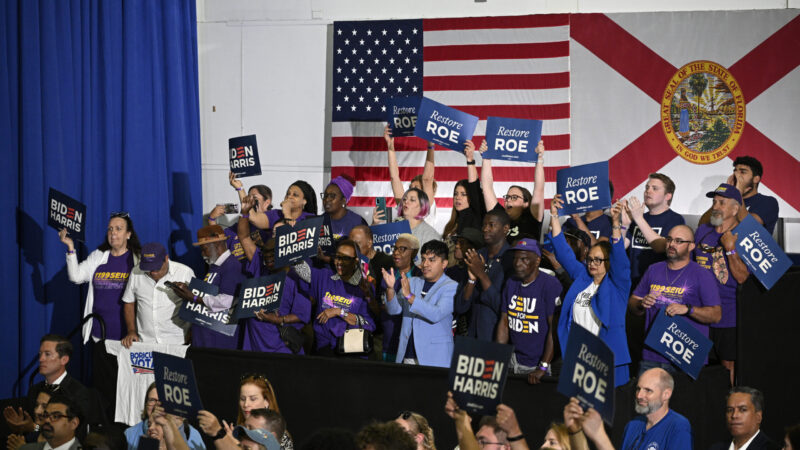
Florida’s 6-week abortion ban will have a ‘snowball effect’ on residents across the South
Abortion rights advocates say the ban will likely force many to travel farther for abortion care and endure pregnancy and childbirth against their will.
Attitudes among Alabama lawmakers softening on Medicaid expansion
Alabama is one of ten states which has not expanded Medicaid. Republican leaders have pushed back against the idea for years.
Birmingham is 3rd worst in the Southeast for ozone pollution, new report says
The American Lung Association's "State of the Air" report shows some metro areas in the Gulf States continue to have poor air quality.
Why haven’t Kansas and Alabama — among other holdouts — expanded access to Medicaid?
Only 10 states have not joined the federal program that expands Medicaid to people who are still in the "coverage gap" for health care
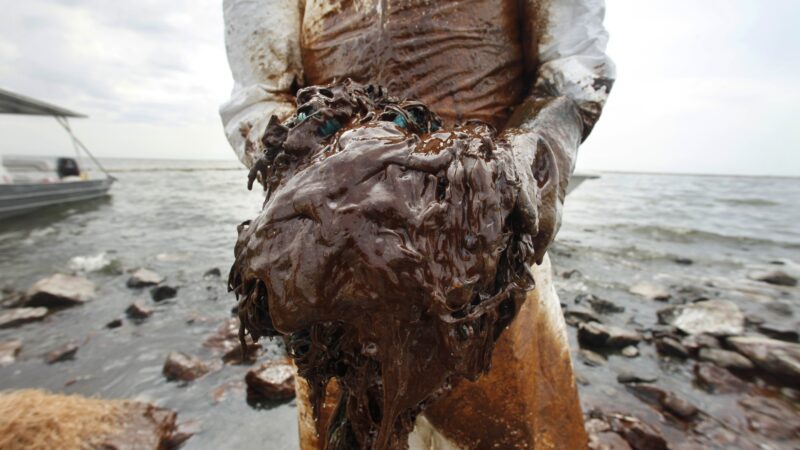
Once praised, settlement to help sickened BP oil spill workers leaves most with nearly nothing
Thousands of ordinary people who helped clean up after the 2010 BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico say they got sick. A court settlement was supposed to help compensate them, but it hasn’t turned out as expected.
Q&A: How harm reduction can help mitigate the opioid crisis
Maia Szalavitz discusses harm reduction's effectiveness against drug addiction, how punitive policies can hurt people who need pain medication and more.